
https://commission.europa.eu

The set of strategic initiatives aimed at guiding the EU in addressing climate change has been named the
European Green Deal, launched by the European Commission in December 2019.
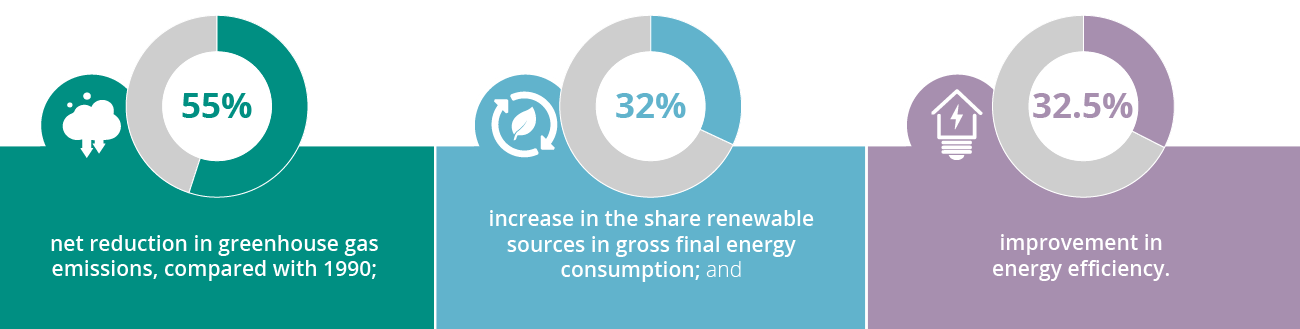
Its goal is to reduce the EU's industrial and energy impact on the environment to zero, with the aim of
achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Specifically, for 2030, the targets are to reduce greenhouse gas
emissions by 55%, increase renewable energy by 32%, and improve energy efficiency by 32.5%.

|
Green Deal InitiativesIndustry
Energy
Other Key Points
Fair Transition Mechanism
|
Energy Transition
11.7% (Forecast 2030)
19% (Updated 2030 Target)
Between 2024 and 2030, the EU must save 1.49% of energy annually, rising to 1.9% by 2030.
|

|
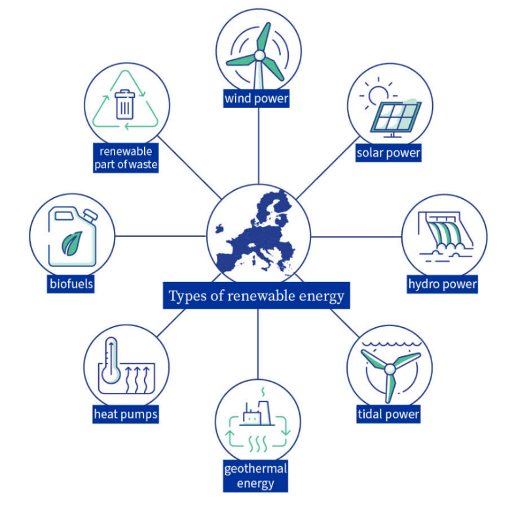
Why Promote Renewable Energy?Renewable energy emits less carbon dioxide than fossil fuels and is generated from abundant, free natural resources. There are various types of renewable energy:
Increasing the share of renewable energy is crucial for:
Since 2005, the gradual replacement of fossil fuels with renewable energy across the EU has led to:
|
|